
In contrast, if there are no cycles in the graph, it means that the system is in a safe state, and resource allocation can proceed If there is a cycle in the graph, it means that the system is in an unsafe state, and granting a resource request can lead to a deadlock. To determine whether the system is in a safe state or not, the RAG is analyzed to check for cycles. A request edge represents a request by a process for a resource, while an assignment edge represents the assignment of a resource to a process. A process node in the RAG has two types of edges, request edges, and assignment edges. It is a directed graph that represents the processes in the system, the resources available, and the relationships between them. Resource Allocation Graph (RAG) is a popular technique used for deadlock avoidance. In this algorithm, a cycle is a necessary but not a sufficient condition for deadlock. When resource categories have multiple instances of their resources, Banker’s Algorithm is used. In this algorithm, a cycle is a necessary and sufficient condition for deadlock. When resource categories have only single instances of their resources, Resource- Allocation Graph Algorithm is used. The system is insecure when no sequence of resource allocation ensures the successful execution of all processes. The successful completion of all processes is not assured, and the risk of deadlock is high. The system attains a safe state when a suitable sequence of resource allocation enables the successful completion of all processes.Ĭonversely, an unsafe state implies a system state where a deadlock may occur. The successful execution of all processes is achievable, and the likelihood of a deadlock is low. Safe State and Unsafe StateĪ safe state refers to a system state where the allocation of resources to each process ensures the avoidance of deadlock.


Deadlock avoidance is a crucial aspect of operating system design and plays an indispensable role in upholding the dependability and steadiness of computer systems.
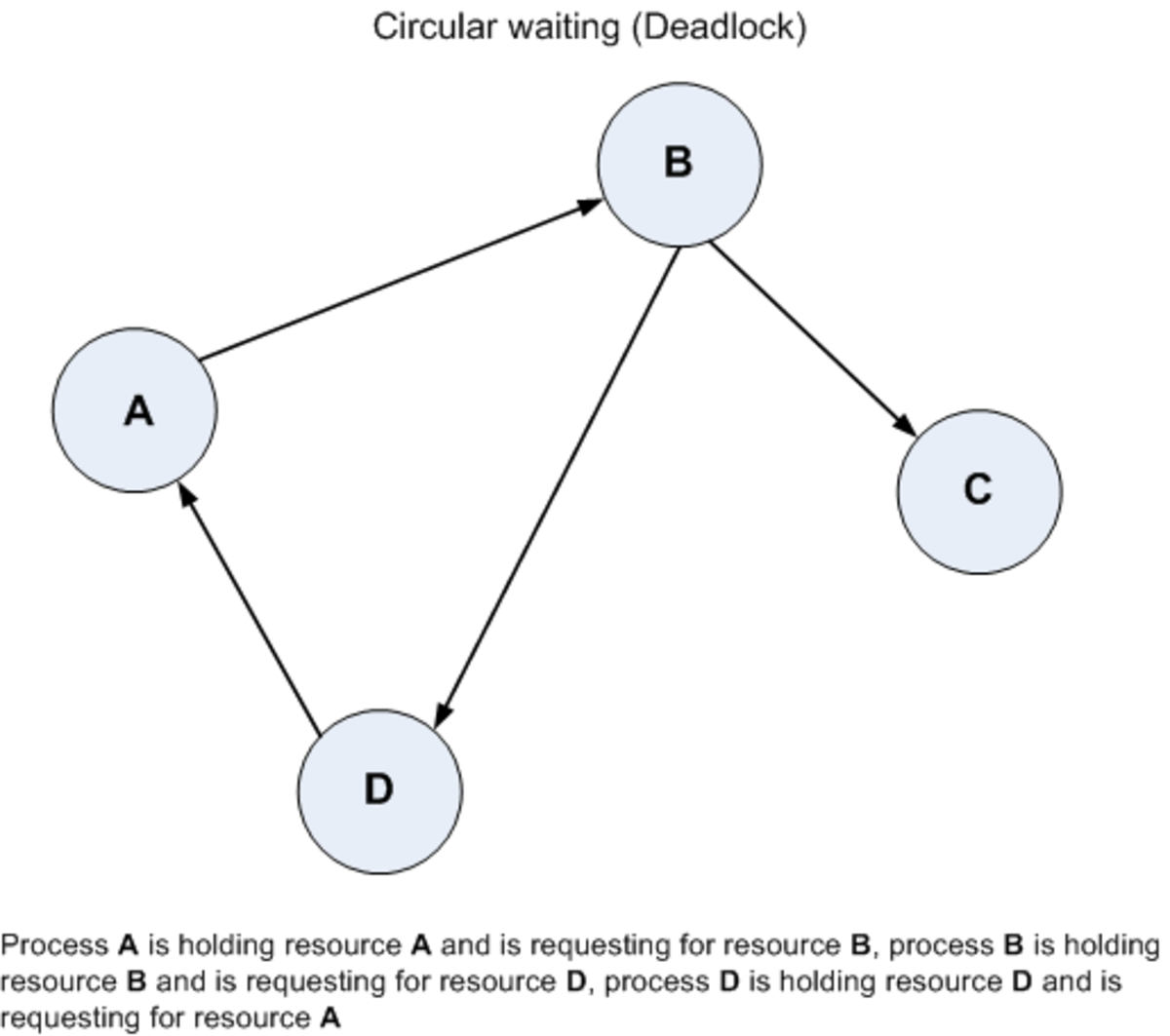
In cases where granting a request would result in a deadlock, the system denies the request. It entails scrutinizing the requests made by processes for resources and evaluating the available resources to determine if the grant of such requests would lead to a deadlock. To prevent such problems, the technique of deadlock avoidance is employed. The resulting deadlocks can cause severe issues in computer systems, such as performance degradation and even system crashes. In complex systems involving multiple processes and shared resources, the potential for deadlocks arises when processes wait for each other to release resources, causing a standstill.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
